3.2 Weight
Mass & Weight, Gravity & Gravitational Field
Weigth
The force exerted on an object by gravity is called weight.
- It is denoted by W.
- Weight is a measure of the gravitational pull on an object by Earth due to gravity.
- The weight of a body varies from place to place.
- It is measured in N (newtons).
- A spring balance/newtonmeter is used to measure the weight

Weight & Gravity
Acceleration due to Gravity
The acceleration produced in the freely falling body due to the earth’s attraction is called acceleration due to gravity.
It is denoted by ‘g’
Weight = mass x acc. due to gravity
W = m × g
(1 N) = (1 kg) × (1 m/s2)
Gravity
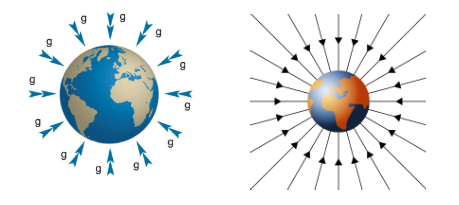
A natural force that pulls all objects toward the centre of the earth is called gravity.
Gravity is a force of attraction that exists between any two objects. Weight acts towards the centre of the planet.
Gravity on the Moon
The acceleration due to gravity, “g,” on the moon is 1.6 m/s2 and 1.6 N/kg because the moon’s mass is less than that of the Earth.

Gravitational Field Strength
The gravitational force (or weight) acting on per unit mass of an object is known as gravitational field strength.

Where ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity 9.8 m/s2 (g ≈ 10 m/s2 on Earth).
The earth’s gravitational field strength pulls everything towards its centre.
Its value is different on different planets because it depends on the mass of the planet.

Figure: Solar system of our Sun
Q: What is the weight of a 12 kg mass on the surface of the Earth and on the surface of the Moon? The value of g on the moon is 1.6 N/kg and 9.8 N/kg on the Earth.
Answer:
WORKED EXAMPLE
Formula of weight W = mg
Weight on the surface of the Earth W = 12 x 9.8 = 117.6 N
Weight on surface of the Moon W = 12 x 1.6 = 19.2 N
- The gravitational force exists between any two objects that have mass.
- The gravitational force is always a force of attraction and never repels.
- The gravitational field is created by the mass of an object.
- The direction of the gravitational field is always towards the centre of the mass.
Worked Example:
The following table shows the weight of 20 kg mass on each first six planets of our solar system.
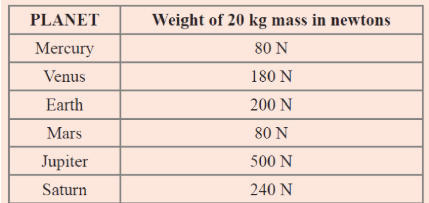
a) Calculate the gravitational field strength of each planet, which is given in the above table.
b) On which planet is the value of gravitational field strength at its maximum?
Answer
In case of planet mercury,

