2.2 Distance & Displacement
Distance
The total length of a path travelled by an object from one place to another place is called distance.
The direction of motion in the case of distance is continuously changing. Distance is a scalar quantity measured in metres.
Displacement
If an object moves from one place to another, the path of the straight line drawn from its initial position to the object’s final position is known as the displacement of the object.
It is the distance between two points in a particular direction, which is defined as
“The shortest and straight-line distance between two points is called displacement”
Displacement is a vector quantity that is always directed from the initial to the final position. It is also measured in metres.
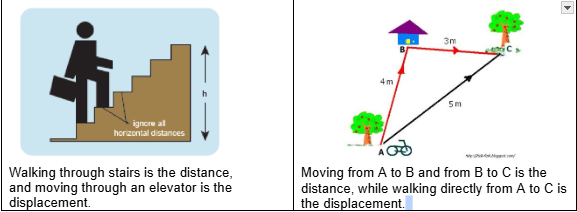
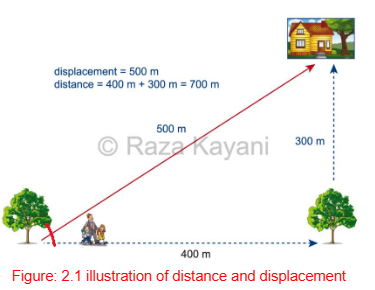
Figure: 2.2 Illustration of distance and displacement
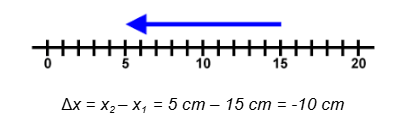
Displacement is a change in position. Displacement can be positive or negative
displacement = final position – initial position
Δx = x2– x1
Positive and Negative Displacements
- In one-dimensional motion, there are only two directions in which an object can move.
- These directions can be stated as positive or negative from the origin.
- Mostly, the right (or eastward) will be considered the positive direction, and the left (or westward) will be considered the negative direction.
- Similarly, upward (or north) will be considered as positive and downward (or south) will be considered as negative.
Positive Displacement
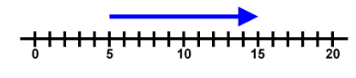
Negative Displacement